Tower Singapore
08:00 - 20:00
- Home
- Machine Tool
HOME > Products & Technology > Products by Market : Machine Tool
Machine Tool
Deep groove ball bearings

The most typical type of bearing, these are used in a wide range of fields. They include grease-enclosed sealed and shield bearings for ease of use.
Other types include bearings with a locating snap-ring to facilitate positioning when mounting the outer ring, expansion compensating bearings that absorb variations in bearing fitting surface dimensions due to housing temperature, and TAB bearings that are resistant to contamination in lubricating oil.
- Related Catalog
-
Angular contact ball bearings
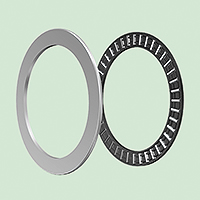
In these ball bearings, the direct line that connects the inner ring, balls, and outer ring has a given angle in the radial direction (the contact angle).
This angle is generally designed with three kinds of contact angle.
These bearings can bear axial loads, but because of the contact angle cannot be used singly and must be used in pairs or combinations.
- Related Catalog
Duplex angular contact ball bearings

These are bearings combining two or more angular ball bearings in back-to-back arrangement, face-to-face arrangement, or tandem arrangement.
Face-to-face duplex (DF) or back-to-back duplex (DB) bearings can bear axial loads in both directions. Back-to-back duplex bearings have a higher moment load bearing capacity than face-to-face duplex bearings. Tandem duplex bearings can bear a larger single-direction axial load than single bearings.
- Related Catalog
Double-row angular contact ball bearings

These have a structure that arranges single row angular contact ball bearings as back-to-back duplex (DB) bearings, uniting both the inner ring and outer ring.
They are able to bear radial loads and bi-directional axial loads, with ability to bear moment loads as well.
Both seal-type and shield-type bearings are available, with rated loads differing from open types.
- Related Catalog
Double-direction thrust angular contact thrust ball bearings
These can support axial loads in both directions, with high rigidity in the axial direction due to a large contact angle. Their structure is not suited to grease-lubricated vertical shafts.
- Related Catalog
High-speed duplex angular contact ball bearings (for axial loads)
These are used in back-to-back duplex (DF) arrangement and can support only bi-directional axial loads. They are superior to double-direction thrust angular ball bearings in high-speed properties, with low axial rigidity.
- Related Catalog
Cylindrical roller bearings

These use rollers as the rolling elements and have a high load capacity. The rollers are guided by the ribs of the inner or outer ring. The inner and outer rings can be separated to facilitate assembly, and both can be fitted tightly.
On types with no ribs, either the inner or the outer ring can move freely in the axial direction, making cylindrical roller bearings ideal for use in free side bearings that absorb shaft expansion.
On types with ribs, the bearing can bear a slight axial load between the roller end surfaces and the ribs. Cylindrical roller bearings include the HT type that modifies the shape of roller end surfaces and ribs to increase axial load capacity, and the E type that has a special internal design to increase radial load capacity. The E type is standard for small-diameter sizes.
- Related Catalog
-
Double row cylindrical roller bearings

These are used in the printing cylinders of printing machinery, rolling mill rolls, and the main shafts of machine tools, where thin-walled bearings are required. In the main shafts of machine tools, the radial inner clearance is adjusted by pushing the tapered shaft into the inner ring of the tapered bore.
- Related Catalog
Tapered roller bearings

Tapered roller bearings are designed so the inner and outer ring raceway and the apex of the tapered rollers intersect at one point on the bearing centerline. For this reason, the rollers are pushed against the inner ring rib and roll guided by the rib, receiving the loads from the inner ring raceway surface and the outer ring raceway surface as a combined load on the raceway surface.
Component force is produced in the axial direction when a radial load is applied, so the bearings must be used in pairs. The inner ring with rollers and outer ring separate, facilitating mounting with clearance or preload. However, assembled clearance is hard to manage and calls for attention. Tapered roller bearings are capable of supporting large loads, both axial and radial.
- Related Catalog
-
Cylindrical roller thrust bearings

These bearings use cylindrical rollers and have single-row, double-row, and three-row types for larger load capacities.
They support axial loads only, are suited to high loads, and have high axial rigidity.
- Related Catalog
Needle roller thrust bearings

These include bearings using machined parts and bearings using pressed steel plate parts for the raceway washer, with the latter type having the smallest cross-sectional height and high load-bearing capacity.
- Related Catalog
-
Ball screw support bearings
- Related Catalog
Clearance adjusting needle roller bearings
- Related Catalog
Complex bearings
- Related Catalog
Cam followers
- Related Catalog
-
Roller followers
- Related Catalog
Linear ball bearings

These are composed of an outer ring, steel balls, and a cage, where the steel balls circulate the ball bearing. The result is a smooth and precise infinite linear motion.
- Related Catalog
Linear roller bearings

These contain cylindrical rollers capable of circulating within the block (orbital unit), enabling smooth linear motion on a flat surface. The cylindrical rollers are retained and guided by the cage (separator) and the ribs of the block.
The construction does not allow contact between adjacent rollers, meaning the friction coefficient is low.
- Related Catalog
Linear flat roller bearings

These are composed of a needle roller integrated into a flat cage. Linear flat roller bearings can be inserted on two planes to ensure smooth reciprocating motion with less friction coefficient.
- Related Catalog
Plastic bearings

Bearings made of resin material for slippery surfaces or axes. Can be adopted for a wide range of fields and machine components due to light weight, lower cost, and versatility compared to metal. Generate less vibration and noise and have a lower slip friction coefficient due to light weight. Excellent plastic workability and electrical insulation when heated, water-resistant.
- Related Catalog
Constant Velocity Joints

Components used to transmit rotational motion so both axes rotate at a constant velocity regardless of the angle between the input and output shaft, and torque is transmitted smoothly (bearings used here).
- Related Catalog
-
Linear Motion Products

Suitable for long stroke transport of both light and heavy objects. Stroke adjustable in units of one millimeter, multiple tables can be combined.
Maintenance
- Related Catalog
-











![Photo: Deep Groove Ball Bearings for High-speed Servo Motors [Type MA]](/content/files/picture/thumb3103.jpg)










![Photo: Sealed Four Row Tapered Roller Bearings for Rolling Mill Roll-Necks [CROU..LL Type]](/content/files/picture/thumb3801.jpg)













