Tower Singapore
08:00 - 20:00
- Home
- Medical Equipment
Medical Equipment
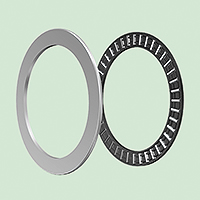
Deep groove ball bearings

The most typical type of bearing, these are used in a wide range of fields. They include grease-enclosed sealed and shield bearings for ease of use.
Other types include bearings with a locating snap-ring to facilitate positioning when mounting the outer ring, expansion compensating bearings that absorb variations in bearing fitting surface dimensions due to housing temperature, and TAB bearings that are resistant to contamination in lubricating oil.
- Related Catalog
-
Angular contact ball bearings
In these ball bearings, the direct line that connects the inner ring, balls, and outer ring has a given angle in the radial direction (the contact angle).
This angle is generally designed with three kinds of contact angle.
These bearings can bear axial loads, but because of the contact angle cannot be used singly and must be used in pairs or combinations.
- Related Catalog
Duplex angular contact ball bearings

These are bearings combining two or more angular ball bearings in back-to-back arrangement, face-to-face arrangement, or tandem arrangement.
Face-to-face duplex (DF) or back-to-back duplex (DB) bearings can bear axial loads in both directions. Back-to-back duplex bearings have a higher moment load bearing capacity than face-to-face duplex bearings. Tandem duplex bearings can bear a larger single-direction axial load than single bearings.
- Related Catalog
Four-point contact ball bearings

These are angular contact ball bearings with the inner ring divided into two. When the outer ring and inner ring are pushed in the radial direction, the balls make contact with the inner ring and outer ring at four points. One bearing is able to bear an axial load from both directions, and can be used in a two-point contact state under a general pure axial load or under a composite load with large axial load.
- Related Catalog
Tapered roller bearings

Tapered roller bearings are designed so the inner and outer ring raceway and the apex of the tapered rollers intersect at one point on the bearing centerline. For this reason, the rollers are pushed against the inner ring rib and roll guided by the rib, receiving the loads from the inner ring raceway surface and the outer ring raceway surface as a combined load on the raceway surface.
Component force is produced in the axial direction when a radial load is applied, so the bearings must be used in pairs. The inner ring with rollers and outer ring separate, facilitating mounting with clearance or preload. However, assembled clearance is hard to manage and calls for attention. Tapered roller bearings are capable of supporting large loads, both axial and radial.
- Related Catalog
-
Double row tapered roller bearings

These have outward-facing types (for double-row outer ring use) and inward-facing types (for double-row inner ring use). As the inner clearance is adjusted to a set value, the bearings must be used in combination with components of the same product number, as marked.
In addition to duplex bearings that combine a pair of single row tapered roller bearings, there are also four-row tapered roller bearings composed of two double-row inner rings, one double-row outer ring, and two single-row outer rings. Four-row tapered outer bearings are used in high-load applications such as rolling mill roll necks.
- Related Catalog
Spherical roller bearings

These bearings have an outer ring with a spherical track surface, and an inner ring that encloses two rows of barrel-shaped rolling elements.
Various types exist that differ by internal design, including bearings with a tapered bore inner caliber. The bearings are easily mounted on the shaft with an adapter or un-mounting sleeve, and are used in many industrial machines for their high load capacity. Potential troubles include one row bearing no load when axial load is large, calling for attention to usage conditions.
- Related Catalog
-
Ultra thin wall type ball bearings
- Related Catalog
Bearings for Special Environments
- Related Catalog
Plastic bearings

Bearings made of resin material for slippery surfaces or axes. Can be adopted for a wide range of fields and machine components due to light weight, lower cost, and versatility compared to metal. Generate less vibration and noise and have a lower slip friction coefficient due to light weight. Excellent plastic workability and electrical insulation when heated, water-resistant.
- Related Catalog
Linear Motion Products

Suitable for long stroke transport of both light and heavy objects. Stroke adjustable in units of one millimeter, multiple tables can be combined.











![Photo: Deep Groove Ball Bearings for High-speed Servo Motors [Type MA]](/content/files/picture/thumb3103.jpg)









![Photo: Sealed Four Row Tapered Roller Bearings for Rolling Mill Roll-Necks [CROU..LL Type]](/content/files/picture/thumb3801.jpg)


![Photo: ULTAGE Spherical Roller Bearings [Type EA, Type EM]](/content/files/picture/thumb3033.jpg)
![Photo: Sealed Spherical Roller Bearings [WA Type]](/content/files/picture/thumb3703.jpg)





